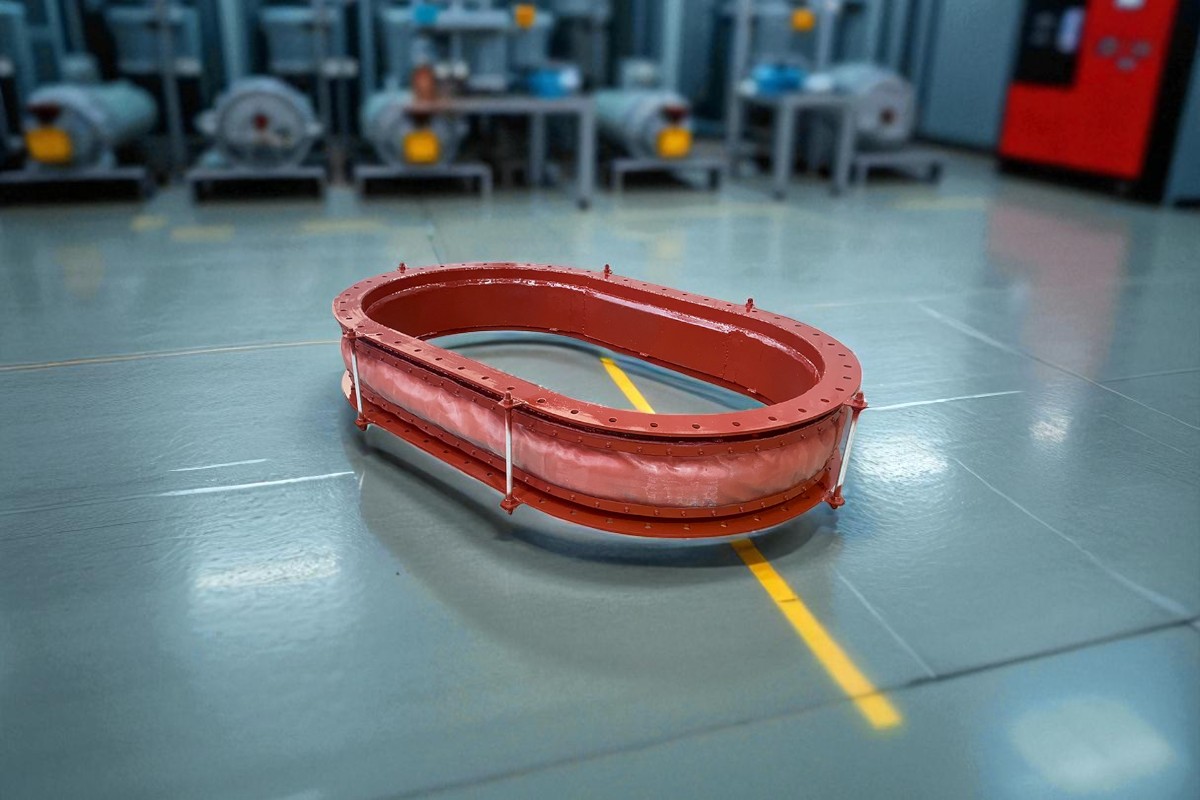
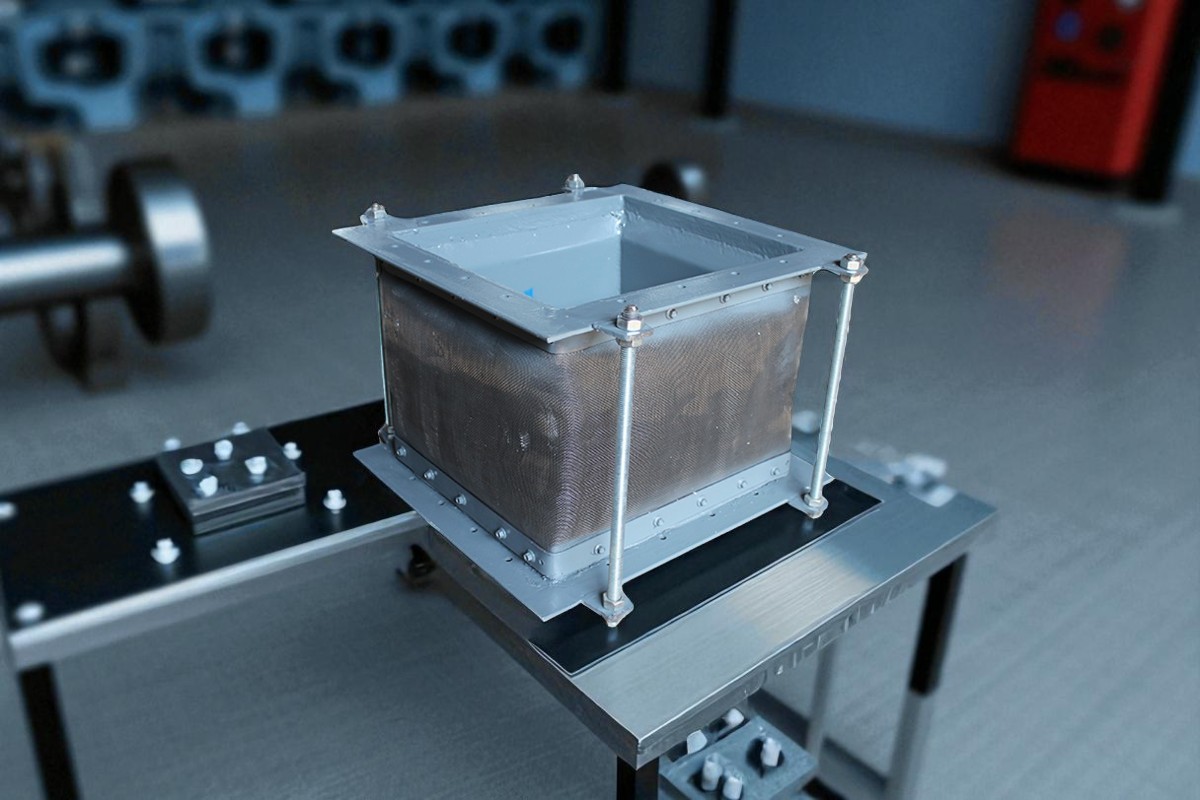
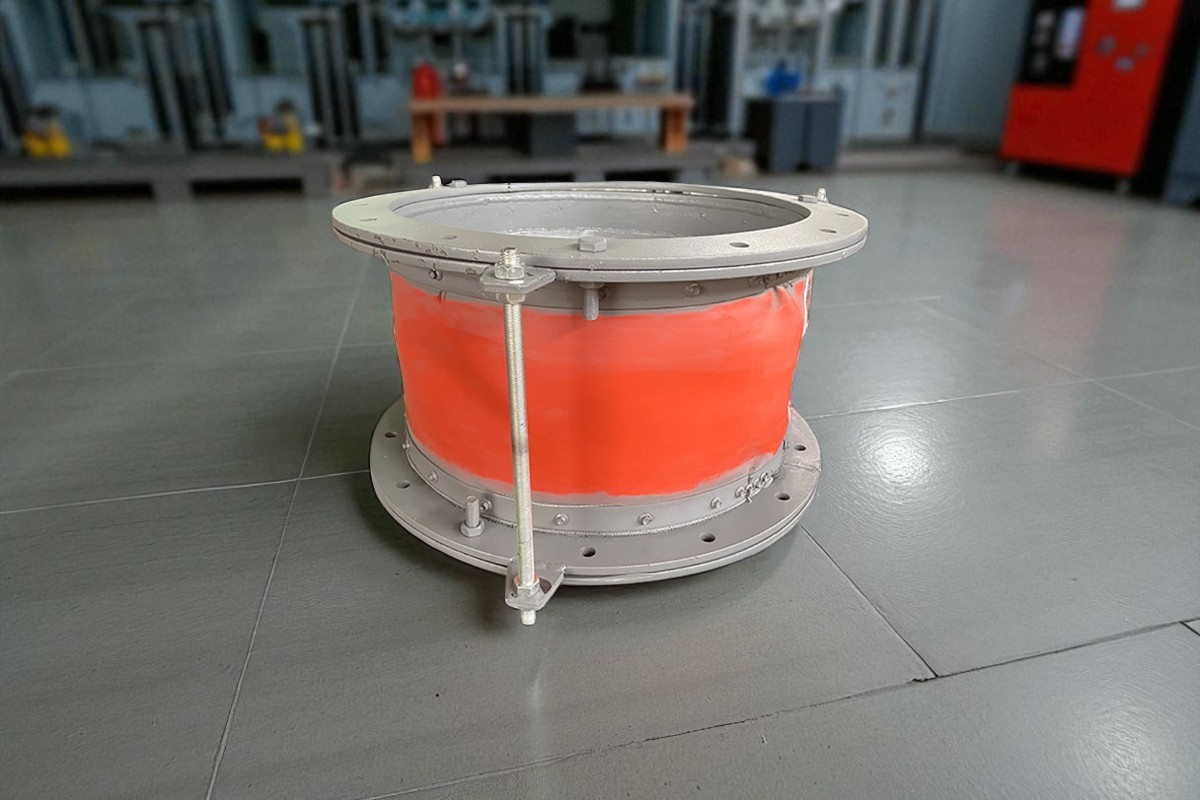
With the increasing demands for sealing performance, temperature resistance, and vibration absorption in modern industrial equipment, non-metallic fabric expansion joints have become widely used in power generation, metallurgy, cement, petrochemical, and other sectors. This article introduces the structure, advantages, typical applications, and installation guidelines of fabric expansion joints to help engineers better understand and apply this essential component.
A non-metallic fabric expansion joint, also known as a fabric compensator or flexible expansion joint, is a multi-layer structure made from high-temperature and corrosion-resistant flexible materials such as PTFE-coated fiberglass cloth, silicone rubber fabric, and fluoroelastomers. It is used to absorb thermal expansion, isolate vibration, compensate for installation deviations, and protect pipeline systems.
Sealing Layer: Typically PTFE or silicone-coated fiberglass fabric, providing excellent sealing and temperature resistance.
Insulation Layer: Made from ceramic fiber or aluminum silicate blanket, used for thermal insulation.
Reinforcement Layer: Enhances structural strength and pressure resistance.
External Protection Layer: Prevents moisture or chemical erosion from the environment.
Stainless Steel Frame or Flow Guide Plate: For high-pressure or high-velocity applications to prevent material blowout.
Excellent Flexibility: Capable of absorbing axial, lateral, angular, and torsional movements.
High Temperature and Corrosion Resistance: Operates from -60°C to +1000°C and resists acidic or corrosive gas.
Vibration and Noise Reduction: Effectively isolates mechanical vibration and noise.
Easy Installation: Lightweight, easy to transport, cut, and install.
No Reaction Force: Does not transfer stress to adjoining equipment.
Cost-effective: Long service life and low overall maintenance cost.
Power Plant Desulfurization Systems: Between boiler and desulfurization/ESP units.
Cement Rotary Kiln Systems: For compensating high-temperature flue gas movement.
Metallurgical Hot Blast Furnaces: Air duct systems requiring vibration isolation.
Petrochemical Equipment Exhaust Systems: Flexible connections with acid/alkaline resistance.
Steel Plant Air Supply Systems: Absorbing pipeline displacement in high-temp ducts.
Confirm Operating Conditions: Temperature, pressure, gas composition, movement directions, installation space.
Material Selection:
Use silicone fabric or ceramic cloth for high-temperature smoke.
Use PTFE-coated cloth for corrosive media.
Dimension Design:
Ensure enough space for movement and compensation range.
Installation Tips:
Leave expansion space; avoid over-compression or stretch.
Protect the insulation layer; prevent condensation.
Flow guide plates should face media direction.
Regularly check bolts and flanges to prevent leakage.
| Feature | Fabric Expansion Joint | Metal Expansion Joint |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Range | -60°C ~ 1000°C | -40°C ~ 600°C |
| Movement Absorption | Excellent | Moderate |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Average |
| Weight | Lightweight | Heavy |
| Maintenance | Easy | Complex |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |